Important reasons why Roundup should be banned forever
07/20/2016 / By JD Heyes

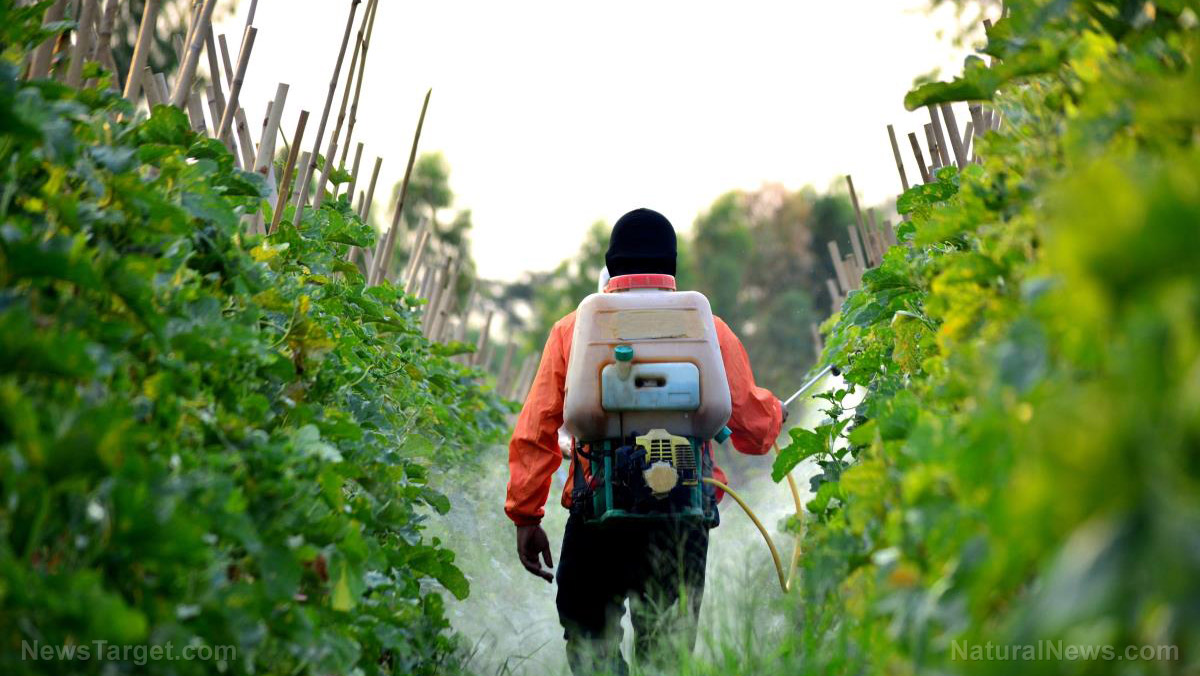
It has long been touted as a harmless chemical that has greatly expanded the world’s crop yields, but the fact is that Roundup herbicide, which is manufactured by Monsanto, is a very deadly compound that persists on and in the food crops we consume.
In fact, there are many consequences that have stemmed from widespread use of Roundup, especially in commercial agriculture, and together they are more than reason enough to ban this toxic chemical forever, for the sake of our environment and for future generations:
Roundup-ready crops absorb its most active ingredient, glyphosate
In spite of industry claims, Roundup doesn’t simply wash off food crops after they have been sprayed. A recent study in Norway found that glyphosate actually accumulates inside crops at excessive levels.
The study, published in the journal Food Chemistry, found that while Roundup Ready crops can resist glyphosate in order to survive, they also absorb the chemical.
Roundup exposure doubles risk of lymphoma
While the government says, as does Monsanto, that glyphosate is basically an inert chemical and that we don’t have anything to fear or worry about, a recent review of more than 44 published scientific studies found that that’s not the case. The meta-analysis of studies determined that exposure to glyphosate doubles your risk of developing non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
Roundup increasing found everywhere
Something to remember is that Roundup is not just isolated to crop fields. Scientists are finding that the chemicals in Roundup are being found in the air and has even tainted rainfall. That means glyphosate is traveling with wind patters and raining down on our homes, and where children play.
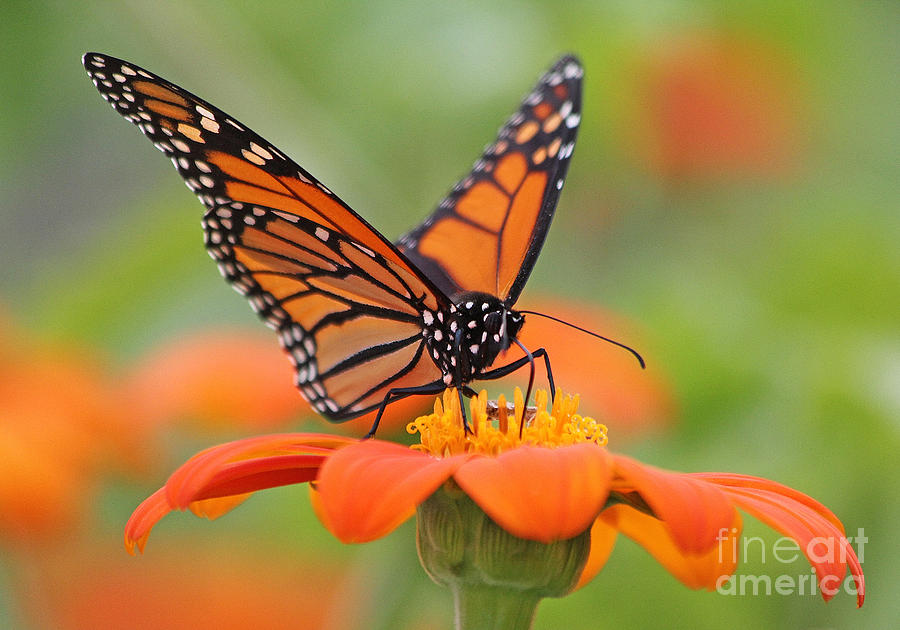
Killing off our pollinators
Iowa State University researchers found that glyphosate use has resulted in an 81 percent reduction in the monarch butterfly population, which relies very heavily on milkweed for survival and reproduction. Like bees, monarch butterflies are crop pollinators; without them, most seed- and fruit-bearing plants and trees could not survive.
Sources:
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author